

Vikram Sarabhai:Often considered the father of the Indian space program, Sarabhai was instrumental in establishing ISRO in 1969. His vision and leadership laid the foundation for India's space exploration endeavors.

Dhawan succeeded Sarabhai as the chairman of ISRO and is credited with transforming it into a world-class space agency. under his guidance, ISRO achieved significant mileston.

A renowned aerospace scientist, Kalam played a pivotal role in the development of India's ballistic missile and launch vehicle technology. also know as missile man
set up by the Government of India, as envisioned by Dr. VikramA Sarabhai.
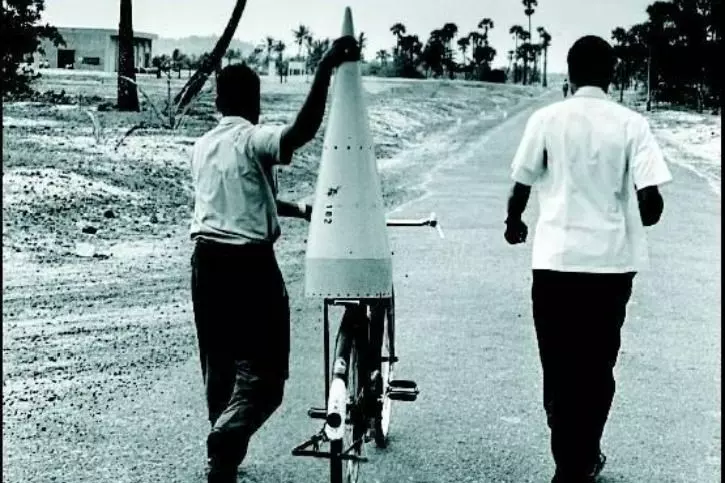


Recognising the need for space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969.
ISRO built India's first satellite, Aryabhata, which was launched by the Soviet space agency Interkosmos in 1975.
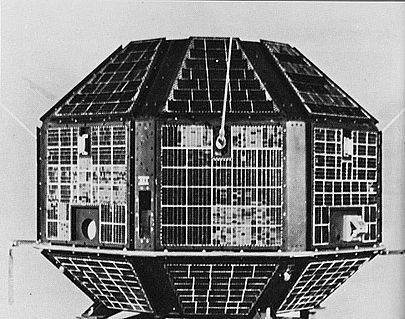
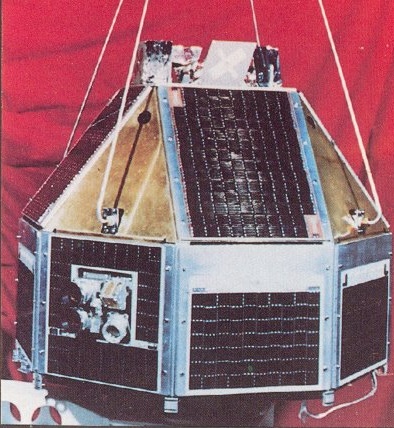
The first satellite to be placed in orbit by an Indian-made launch vehicle (SLV-3).
He is the only Indian citizen to travel in space, although there have been other astronauts of Indian origin who travel space


Recognising the need for space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969.
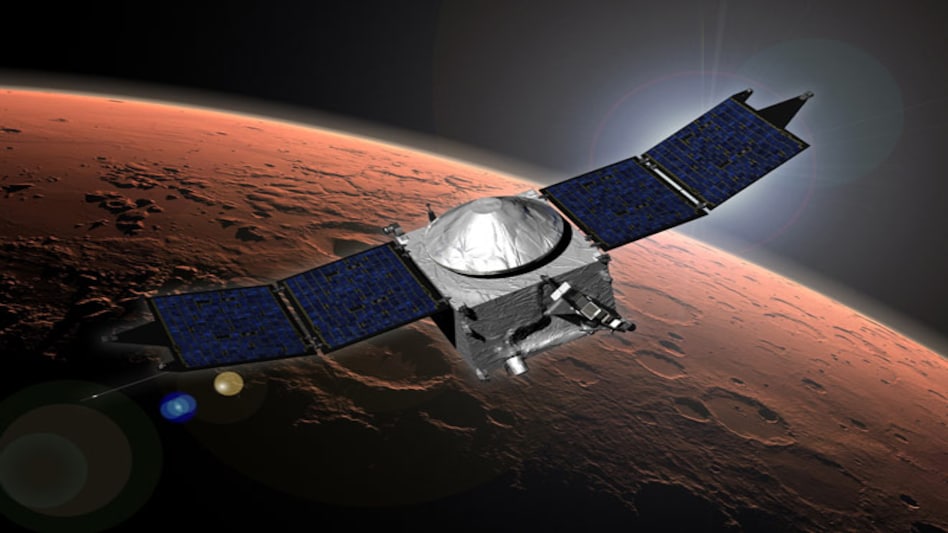
Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India's first interplanetary mission to planet Mars was launchedonboard PSLV-C25 on November 05, 2013.


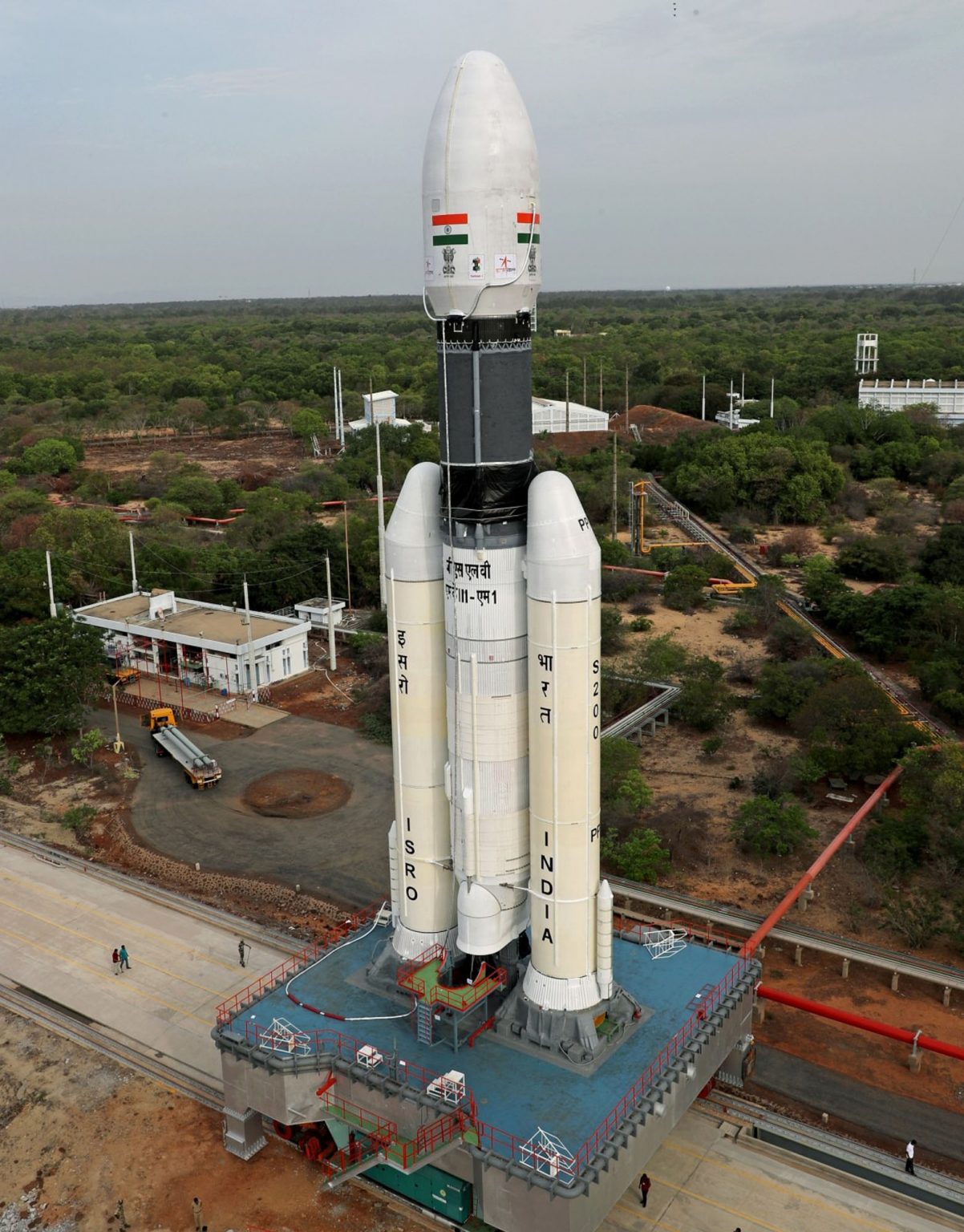
the rocket successfully carried and deployed a record number of 104 satellites in Sun-synchronous orbits in a single mission
which brought together an Orbiter, Lander and Rover with the goal of exploring south pole of the Moon.
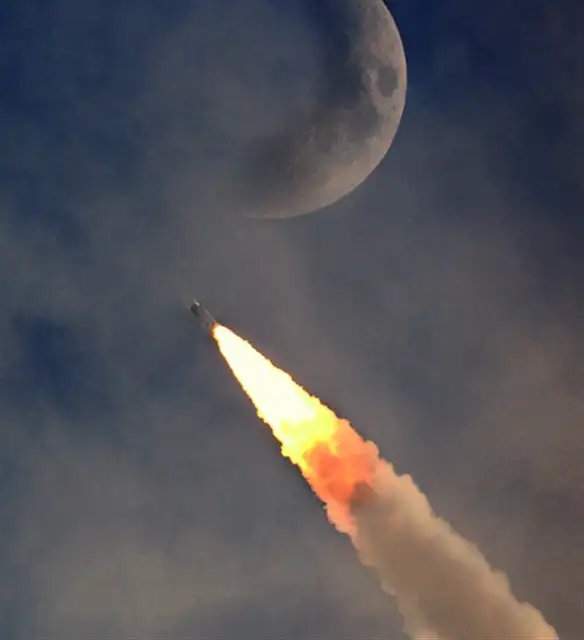


Chandrayaan-3 successfully lands on the lunar south pole, making India the fourth country to achieve a soft landing on the Moon and the first to do so near the lunar south pole